3.0 KiB
3.0 KiB
Singleton for simple logging
Basic Usage
import singlog;
void main(string[] argv) {
log.output(log.SYSLOG | log.STDOUT | log.FILE) // write to syslog, standard output stream and file
.program(argv[0]) // program name as an identifier (for Windows OS)
.level(log.DEBUGGING) // logging level
.color(true) // color text output
.file("./test.log"); // the path to the log file
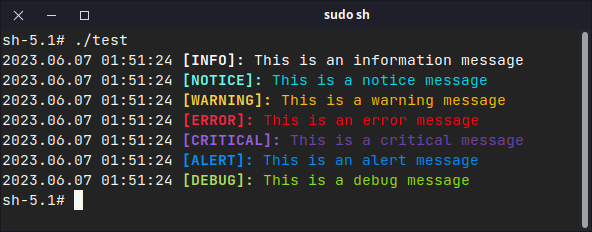
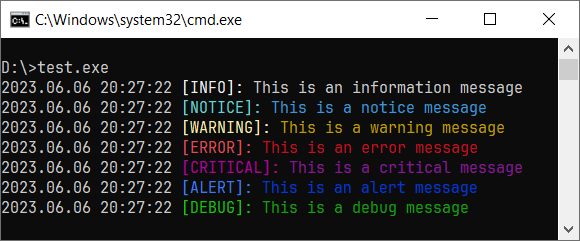
log.i("This is an information message");
log.n("This is a notice message");
log.w("This is a warning message");
log.e("This is an error message");
log.c("This is a critical message");
log.a("This is an alert message");
log.d("This is a debug message");
}
Examples
Setting the name of the logged program (it matters for Windows OS):
log.program("My program");
Setting the status of color text output (false by default):
log.color(true);
Setting the error output level:
log.level(log.DEBUGGING);
log.level(log.ALERT);
log.level(log.CRITICAL);
log.level(log.ERROR);
log.level(log.WARNING);
log.level(log.NOTICE);
log.level(log.INFORMATION);
Assigning a target output:
log.output(log.SYSLOG);
log.output(log.STDOUT);
Setup and allowing writing to a file:
log.output(log.FILE);
log.file("./file.log");
Output of messages to the log:
log.a("Alert message") => log.alert("Alert message");
log.c("Critical message") => log.critical("Critical message");
log.e("Error message") => log.error("Error message");
log.w("Warning message") => log.warning("Warning message");
log.n("Notice message") => log.notice("Notice message");
log.i("Information message") => log.information("Information message");
log.d("Debugging message") => log.debugging("Debugging message");
DUB
Add a dependency on "singlog": "~>0.4.0".