|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| man | ||
| source | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| dub.json | ||
| dub.selections.json | ||
| dub.settings.json | ||
| logo.png | ||
| singlog.png | ||
README.md
Singleton Logging Module
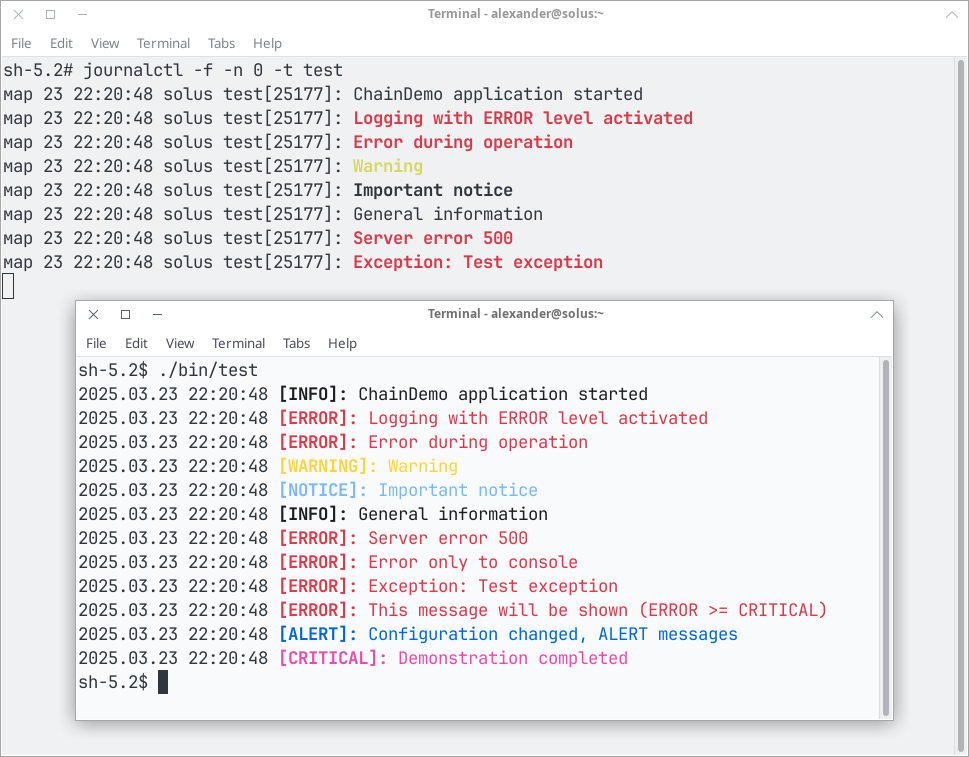
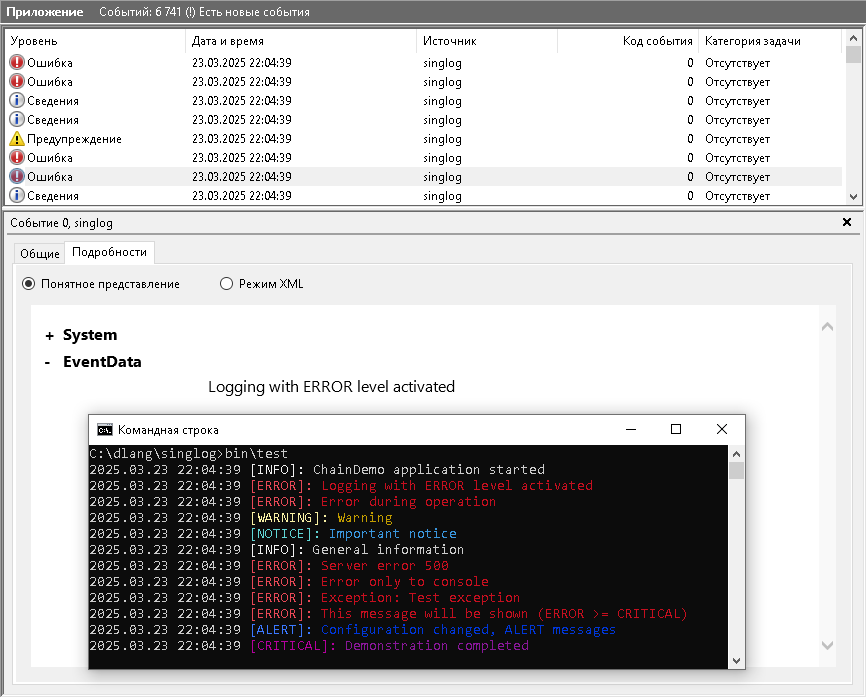
singlog is a singleton logging module written in the D programming language, designed to provide thread-safe, cross-platform logging with flexible output targets. It supports multiple log levels, configurable output destinations (syslog, console, file), and optional colored console output, making it a versatile tool for application logging.
Features
- Thread-Safety: Utilizes a
Mutexto ensure safe logging in multi-threaded applications. - Cross-Platform: Works on both Windows (Event Log, console) and POSIX (syslog, console) systems.
- Flexible Output Targets: Supports logging to:
- System logs (syslog on POSIX, Event Log on Windows).
- Standard output (
stdoutfor NOTICE and above,stderrfor ERROR and below). - Files (with configurable file paths).
- Log Levels: Seven configurable levels:
DEBUGGING(highest priority)ALERTCRITICALERRORWARNINGNOTICEINFORMATION(lowest priority)
- Fluent Interface: Provides a chaining API for easy configuration of output targets, log levels, and settings.
- Colored Output: Optional ANSI color support for console messages (on POSIX) or Windows console colors.
- Singleton Design: Ensures a single logger instance throughout the application, accessible via
Log.msgor thelogalias. - Aliases: Short aliases (e.g.,
dfordebugging,eforerror) for concise logging.
Installation
To use singlog, include it in your D project:
-
Via Source: Copy the
singlog.dfile into your project’s source directory. -
Via DUB (if packaged):
Add it to your
dub.json:"dependencies": { "singlog": "~>1.0.0" }
Usage
Basic Configuration and Logging
The singlog module provides a singleton logger instance accessible via Log.msg or the global log alias. Here’s a basic example:
import singlog;
void main() {
// Configure the logger
log.program("MyApp") // Set program name for syslog/Event Log
.color(true) // Enable colored console output
.level(log.level.debugging) // Set minimum log level to DEBUGGING
.output(log.output.std.file.syslog) // Output to console, file, and syslog
.file("./myapp.log"); // Set log file path
// Log messages
log.debugging("Starting application in debug mode");
log.information("Initialization complete");
log.error("Failed to load resource");
}
This configures the logger to:
- Identify as "MyApp" in system logs.
- Use colored output on the console.
- Log all messages (from
DEBUGGINGup). - Write to the console, a file (
myapp.log), and the system log.
Log Levels and Aliases
The logger supports seven log levels with corresponding methods and aliases:
| Level | Method | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
DEBUGGING |
debugging() |
d() |
Debugging information |
ALERT |
alert() |
a() |
High-priority alerts |
CRITICAL |
critical() |
c() |
Critical errors |
ERROR |
error() |
e() |
General errors |
WARNING |
warning() |
w() |
Warnings |
NOTICE |
notice() |
n() |
Notices |
INFORMATION |
information() |
i() |
Informational messages |
Example using aliases:
log.d("Debug message");
log.i("Info message");
log.e("Error message");
Output Targets
Output targets can be configured using the output() method and its fluent interface:
syslog(): Logs to the system log (Event Log on Windows, syslog on POSIX).std(): Logs to the console (stdoutorstderrbased on log level).file(): Logs to a file (requiresfile()to set the path).
Example:
log.output(log.output.std.file); // Console and file output
log.i("This goes to console and file");
Temporary Output Override
Use now() to temporarily override output targets for the next log call:
log.now(log.output.std).n("This goes only to console");
log.i("This uses default outputs again");
Colored Output
Enable colored output with color(true):
log.color(true);
log.w("This warning will be yellow on POSIX or Windows");
log.c("This critical message will be magenta");
Colors differ by platform:
- POSIX: Uses ANSI escape codes (e.g., green for
DEBUGGING, red forERROR). - Windows: Uses console color attributes (e.g., yellow for
WARNING, white forINFORMATION).
File Logging
Set a log file with file():
log.file("app.log");
log.e("This error goes to app.log");
The file is opened in append mode ("a+") and includes timestamps.